Machine Learning General Questions
MACHINE LEARNING QUESTIONS
1. What are the different types of Machine Learning?
- Supervised Learning
- machine lears using labeled data
- it’s like learning under the guidace of a teacher
- model is trained on pre-defined dataset before it starts making decision when given new data
- Unsupervised Learning
- the machine is trained on unlabelled data, without any guidance
- learning without a teacher
- models learn through observation and finds structures in data
- model is given a dataset and then left to automatically find patterns and relationships by creating clusters
- Reinforcement Learning
- involves an agent that interacts with its environment by producing actions & discovers errors or rewards’- it’s like being stuck in an isolated island where you must explore the environment and learn how to live and adapt to the living conditions on your own
- model learns through hit and trial method
- learns on the basis of reward or penalty given for every action it performs
2. How would you explain Machine Learning to a school-going kid?
- Suppose your friend invites you to his party where you meet total strangers. Since you have no idea about them, you will mentally classify them on the basis of gender, age, group, dressing, etc.
- in this scenari the strangers represent the unlabelled data and the process od classifying unlabelled data point (unsupervised learning)
- since you didn’t use any prior knowledge abut people and classified them on-the-go, this becomes an unsupervised learning problem.
3. How does Deep Learning differ from Machine Learning?
-
DEEP LEARNING - form of ML that is inspired by the structure of the human brain and is particulary effective in feature detection.
-
MACHINE LEARNING - algorithms that parse data, learn from data, and then apply what they’ve learnt to make informed decisions.
4. Explain Classification and Regression
- Classification:
- predicting a discrete class label
- data is labelled into one of two or more class
- two classes -> binary, more -> multi-class classification
- examples: classifying email as SPAM or non-SPAM
- Regression:
- predicting a continous quantity
- requires the prediction of a quantity
- if it has multiple input variables it’s called a multivariate regression
- examples: predicting the price of a stock over a period of time
5. What do you understand by selection bias?
- statistical error that causes a bias in the sampling portion of an experiment
- the error causes one sampling group to be selected more often than other groups included in the experiment
-
selection bias may produce an inaccurate conclusion if the selection bias is not identified
- błąd statystyczny, który powoduje odchylenie w próbkowaniu części eksperymentu
- błąd powoduje, że jedna grupa losowania jest wybierana częściej niż inne grupy objęte eksperymentem
- błąd selekcji może prowadzić do niedokładnych wniosków, jeśli błąd selekcji nie zostanie zidentyfikowany
6. What do you understand by Precision and Recall?
Let me explain you this with an analogy:
Imagine that, your girlfriend gave you a birthday surprise every year for the last 10 years. One day, your girlfriend asks you: ‘Sweetie, do you remember all the birthday surprises from me?’ To stay on good terms with your girlfriend, you need to recall all the 10 events from your memory. Therefore, recall is the ratio of the number of events you can correctly recall, to the total number of events.
If you can recall all 10 events correctly, then, your recall ratio is 1.0 (100%) and if you can recall 7 events correctly, your recall ratio is 0.7 (70%).
However, you might be wrong in some answers.
For example, let’s assume that you took 15 guesses out of which 10 were correct and 5 were wrong. This means that you can recall all events but not so precisely.
Therefore, precision is the ratio of a number of events you can correctly recall, to the total number of events you can recall (mix of correct and wrong recalls).
From the above example (10 real events, 15 answers: 10 correct, 5 wrong), you get 100% recall but your precision is only 66.67% (10 / 15)
7. Explain false negative, false positive, true negative and true positive with a simple example.
Scenario of a fire emergency:
- True Positive: If the alarm goes on in case of a fire.
FIRE IS POSITIVE AND PREDICTION MADE BY THE SYSTEM IS TRUE
- False Positive: if the alarm goes on and there is no fire.
SYSTEM PREDICTED FIRE TO BE POSITIVE WHICH IS A WRONG PREDICTION HENCE THE PREDICTION IS FALSE
- False Negative: If the alarm does not ring but there was a fire.
SYSTEM PREDICTED FIRE TO BE NEGATIVE WHICH WAS FALSE SINCE THERE WAS FIRE.
- True Negative: If the alarm does not ring and there was no fire
THE FIRE IS NEGATIVE AND THIS PREDICTION WAS TRUE
8. What is a Confusion Matrix?
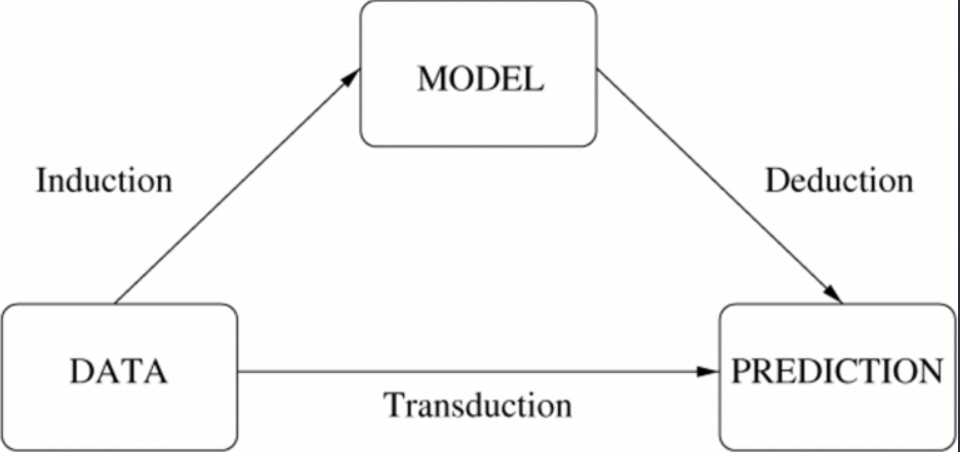
9. What is the difference between inductive and deductive learning?
-
Inductive learning is the process of using observations to draw conclusions
-
Deductive learning is the process of using conclusions to form observations
10. How is KNN different from K-means clustering?
- K-Nearest Neighbour
- Supervised Technique
- Used for Classification or Regression
- “K” in KNN represents the number of nearest neighbours used to classify or predict in case of continous variable/regression
- K-Means Clustering
- Unsupervised Technique
- Used for Clustering
- “K” in K Means represent the number of clusters the algorithm is trying to identify or learn from the data
11. What is ROC curve and what does it represent?
Receiver Operating Characteristic curve is a fundamental tool for diagnostic test evaluation and is a plot of the true positive rate (Sensivity) against the false positive rate (Specifity) for the different possible cut-off points of a diagnostic test.
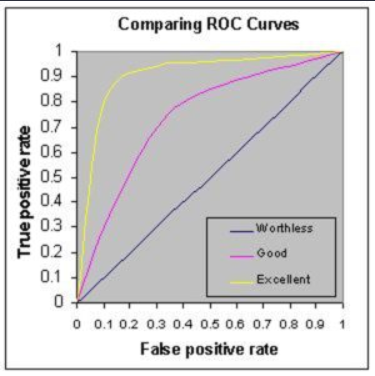
- it shows the trade-off between sensitivity and specifity (any increase in sensitivity will be accompanied by a decrease in specifity)
- the closer the curve follows the left-hand border and then the top border of the ROC space